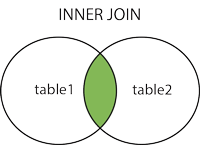
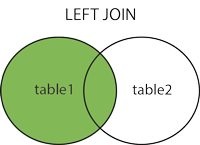
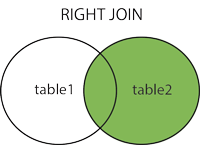
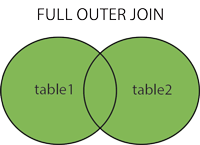
The JOIN expression is used to join rows from two or more tables based on the related column between them.
Let's look at a sample from the table "Orders" ("Orders"):
| ProductID | OrderID | CustomerID | EmployeeID | OrderDate | ShipperID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10248 | 90 | 5 | 1996-07-04 | 3 |
| 2 | 10249 | 81 | 6 | 1996-07-05 | 1 |
| 3 | 10250 | 34 | 4 | 1996-07-08 | 2 |
Then look at the sample from the table "Customers" ("Customers"):
| CustomerID | CustomerName | ContactName | Address | City | PostalCode | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alfreds Futterkiste | Maria Anders | Obere Str. 57 | Berlin | 12209 | Germany |
| 2 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | Ana Trujillo | Avda. de la Constitución 2222 | México D.F. | 5021 | Mexico |
| 3 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | Antonio Moreno | Mataderos 2312 | México D.F. | 5023 | Mexico |
Note that column "CustomerID" in table "Orders" refers to "CustomerID" in table "Customers". The relationship between the two tables above is the "CustomerID" column.
We can then create the following SQL statement (containing INNER JOIN) that selects records that have matching values in both tables:
Run SQLSELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID
and this will produce something like this:
| OrderID | CustomerName | OrderDate |
|---|---|---|
| 10308 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | 1996-09-18 |
| 10365 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | 1996-11-27 |
| 10355 | Around the Horn | 1996-11-15 |
| 10383 | Around the Horn | 1996-12-16 |
| 10289 | B's Beverages | 1996-08-26 |
Here are the different types of JOIN in SQL: